Freeware isn’t actually free software, and we’re all paying for it now. We regularly tell our customers to be very careful when installing free software because it generally carries a hidden payload of crappy software with it.
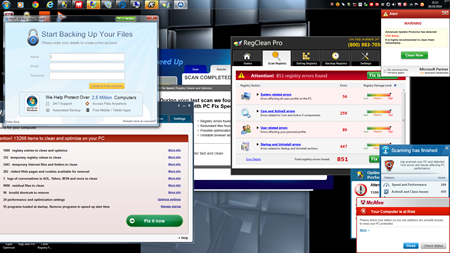
Most computer tune-ups we perform for our customers begin with the removal of a bunch of free, useless programs that are sapping the life out of our customer’s computers. In most cases they did not even install this pesky software, they installed something else that snuck the bad software into their computer as a hidden payload.
The folks over at http://www.howtogeek.com went to the leading software download sites and grabbed the top ten software recommendations and here is what happened when they installed it. Check out the results, you will be surprised. Do you and your computer a favor and stay clear of free software, when it comes to software, you really do get what you pay for.





 Who hasn’t received an email directing them to visit a familiar website where they are being asked to update their personal information? The website needs you to verify or update your passwords, credit card numbers, social security number, or even your bank account number. You recognize the business name as one that you’ve conducted business with in the past. So, you click on the convenient “take me there” link and proceed to provide all the information they have requested. Unfortunately, you find out much later that the website is bogus. It was created with the sole intent to steal your personal information. You, my friend, have just been “phished”.
Who hasn’t received an email directing them to visit a familiar website where they are being asked to update their personal information? The website needs you to verify or update your passwords, credit card numbers, social security number, or even your bank account number. You recognize the business name as one that you’ve conducted business with in the past. So, you click on the convenient “take me there” link and proceed to provide all the information they have requested. Unfortunately, you find out much later that the website is bogus. It was created with the sole intent to steal your personal information. You, my friend, have just been “phished”. When it comes to computer security, many of us live in a bubble of blissful ignorance. We might be vigilant and never open email attachments from people we don’t know, we might take care to make sure an eCommerce site is secure before entering our credit card information, or we might even go so far as to install a standard firewall on our computers. Unfortunately, much of the common sense advice we follow when it comes to Internet security does little to combat the cybercrime that is rampant.
When it comes to computer security, many of us live in a bubble of blissful ignorance. We might be vigilant and never open email attachments from people we don’t know, we might take care to make sure an eCommerce site is secure before entering our credit card information, or we might even go so far as to install a standard firewall on our computers. Unfortunately, much of the common sense advice we follow when it comes to Internet security does little to combat the cybercrime that is rampant.